Rails and Devise: Security settings
Devise is probably the best known, and most widely used Ruby gem for adding authentication to a Rails app. It’s just simply great. It’s creates the views for the login pages, adds convenient methods for authenticating users in the controllers, and even has a generator to create the user model. It is also highly configurable, and in this post we’ll take a look at some of the configurations that allow us to make simple security improvements to a Rails app.
Avoiding user enumeration with paranoid mode
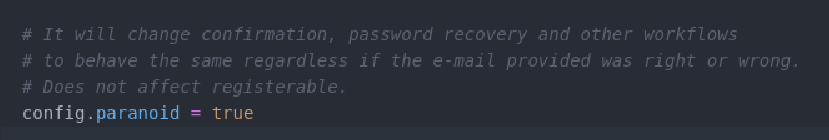
To avoid user enumeration we want to give a generic message to the users, that doesn’t reveal if a user exists or not. Devise has a paranoid config, that does just that. In a Rails app with Devise installed this can be found in config/initializers/devise.rb.
We can see if we insert an invalid email into the password recovery page, the message doesn’t confirm if the user exists or not.

paranoid = true is the default in later versions of Devise, but in earlier versions it defaults to false. We can
see what happens when paranoid is set to false; a message revealing whether the email corresponds to a valid user or not is returned.
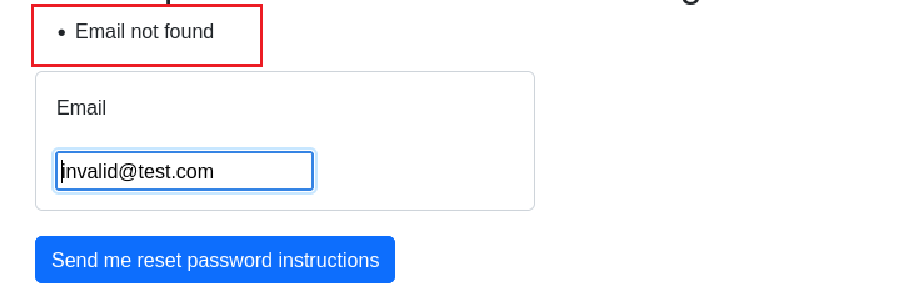
In this case the password recovery page can be easily used to enumerate valid users or not, helping an attacker compile a list of candidates for password attacks. It’s a quick and easy fix to set paranoid to true, and is a great security improvement.
Limiting the amount of retries
The default lock strategy for Devise is based on the numbe of failed login attempts. The default threshold for locking access is unusually high 20 attempts!
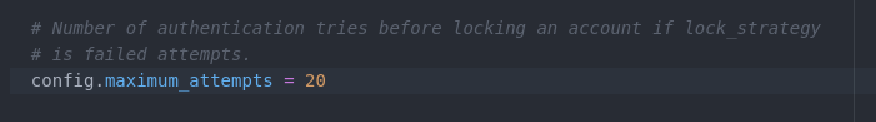
It’s a good idea to reduce this number to something more reasonable like 3.
Conclusion
So we’ve seen just a couple security settings; there are many more options to improve the security of your web applications authentication. I recommend taking a look at the Devise documentation to see what best applies to your case. That being said, setting the amount of failed attempts, and making sure paranoid mode is enabled are two easy wins.